SPEAR:
Speculative
Pre-Execution
Assisted
by compileR
Speculative pre-execution is a new data-prefetching technique which uses an auxiliary assisting thread in addition to the main program flow. A prefetching thread (p-thread), which contains the future probable cache miss instructions and backward slice, can run on the spare hardware context for data prefetching. Recently, various forms of speculative pre-execution have been developed, including hardware-based and software-based approaches.
SPEAR is a pre-execution model which is a hybrid of the two approaches. It relies on a "post-compiler" to extract the p-thread code from program binaries and uses specially designed SMT hardware to trigger the execution of the p-thread dynamically.
Our performance results on 15 memory intensive benchmarks show that our SMT-based SPEAR architecture achieves a 12.7% improvement with the 128 IFQ and a 20.1% with the 256 IFQ. Also, the dedicated resource mode results in an 18.9% and 26.3% speedup with the above two IFQ sizes.
Hardware Description
of the SPEAR
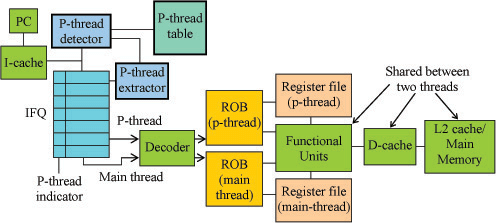
The Operation of the SPEAR Compiler
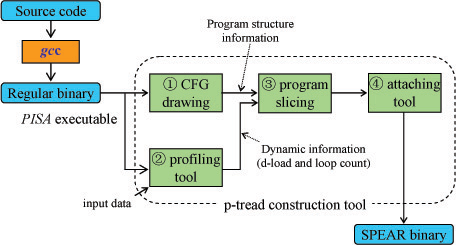
Compiler Support for Dynamic
Speculative Pre-Execution
![]()
![]()
Won W. Ro and Jean-Luc Gaudiot
The 7th Annual Workshop on Interaction between Compilers and Computer
Architectures (INTERACT-7) in conjunction with HPCA-9, Anaheim,
California, February 8, 2003
SPEAR: A Hybrid Model for Speculative
Pre-Execution
![]()
![]()
Won W. Ro and Jean-Luc Gaudiot
Proceedings of 18th International Parallel and
Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS 2004), Eldorado Hotel, Santa Fe,
New Mexico, April 26-30, 2004